回溯
思想
回溯就是使用暴力搜索,利用递归和for循环返回所有满足需求的答案,可以用于解决组合、切割、子集、排列、N皇后等问题。回溯发生在递归时,处理完一种情况后需要在答案中撤销当前情况,便于加入以后的数据得到新的答案。
模板
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
class backtracking {
private:
全局变量 ans 用于保存满足要求的答案
public:
// 递归调用该函数进行暴力搜索并进行回溯操作
void dfs(参数) {
if (终止条件) {
收集结果到ans中保存
return;
}
for (集合元素) {
处理结点
递归调用dfs()
*回溯操作*
}
return;
}
};
|
例题
93. 复原 IP 地址
306. 累加数
二分查找
二分搜索高效的本质在于每次排除可能的空间比顺序遍历更大。在一个有序排列中,首先应想到用二分查找。
标准二分查找模板
左闭右闭
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
class BinarySearch {
public:
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.size() - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
if (nums[mid] == target)
return mid;
if (nums[mid] > target)
right = mid - 1;
else if (nums[mid] < target)
left = mid + 1;
}
return -1;
}
};
|
-
查找范围为[left, right],为闭区间;
-
循环条件:left <= right,需要包括相等的情况;
-
右边界更新:right = mid - 1,左边界更新:left = mid + 1;
-
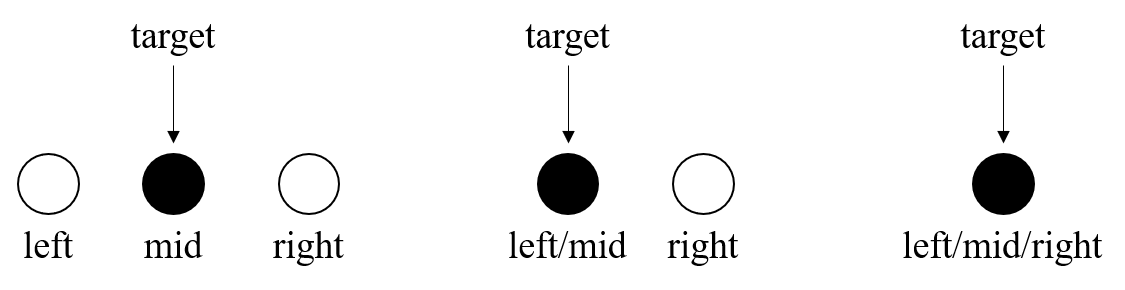
left + ((right -left) >> 1) 对于目标区域长度为奇数而言,是处于正中间的,对于长度为偶数而言,是中间偏左的。因此左右边界相遇时,只会是以下两种情况:
left/mid,right(left,mid指向同一个数,right指向它的下一个数);left/mid/right(left,mid,right指向同一个数)。
-
命中时,会有以下三种情况:


可以得到以下两种结果:

左闭右开
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
class BinarySearch {
public:
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.size();
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
if (nums[mid] == target)
return mid;
if (nums[mid] > target)
right = mid;
else if (nums[mid] < target)
left = mid + 1;
}
return -1;
}
};
|
- 查找范围为
[left, right),右边为开区间;
- 循环条件:
left < right,不包括相等的情况;
- 右边界更新:
right = mid,左边界更新:left = mid + 1;
- 命中时,会有以下两种情况:


可以得到以下两种结果:

例题
875. 爱吃香蕉的珂珂
2064. 分配给商店的最多商品的最小值
1414. 和为 K 的最少斐波那契数字数目
字典树/前缀树/Trie

模板
定义类Trie
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
class Trie {
private:
bool isEnd;
vector<Trie*> next;
public:
Trie() : isEnd(false), next(26) {}
//方法将在下文实现...
};
|
插入
描述:向Trie中插入一个单词word。
实现:这个操作和构建链表很像。首先从根结点的子结点开始与word第一个字符进行匹配,一直匹配到前缀链上没有对应的字符,这时开始不断开辟新的结点,直到插入完word的最后一个字符,同时还要将最后一个结点isEnd = true;,表示它是一个单词的末尾。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
void insert(string word) {
Trie* node = this;
for (auto &ch : word) {
if (!node->next[ch-'a']) {
node->next[ch-'a'] = new Trie();
}
node = node->next[ch-'a'];
}
node->isEnd = true;
}
|
查找
描述:查找Trie中是否存在单词word。
实现:从根结点的子结点开始,一直向下匹配即可,如果出现结点值为空就返回false,如果匹配到了最后一个字符,那我们只需判断node->isEnd即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
bool search(string word) {
Trie* node = this;
for (auto &ch : word) {
node = node->next[ch-'a'];
if (!node) {
return false;
}
}
return node->isEnd;
}
|
例题
208. 实现 Trie (前缀树)
211. 添加与搜索单词 - 数据结构设计
并查集
并查集(英文:Disjoint-set data structure,直译为不交集数据结构)是一种数据结构,用于处理一些不交集(Disjoint sets,一系列没有重复元素的集合)的合并及查询问题。并查集支持如下操作:
由于支持查询和合并这两种操作,并查集在英文中也被称为联合-查找数据结构(Union-find data structure)或者合并-查找集合(Merge-find set)。
模板
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
class UnionFind {
public:
vector<int> parent;
vector<int> ranker;
UnionFind(int _n): parent(_n), ranker(_n, 1) {
iota(parent.begin(), parent.end(), 0);
}
int find(int x) {
if (parent[x] == x)
return x;
parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
return parent[x];
}
bool unionElement(int x, int y) {
int fx = find(x), fy = find(y);
if (fx == fy)
return false;
if (ranker[fx] < ranker[fy])
swap(fx, fy);
parent[fy] = fx;
if (ranker[fx] == ranker[fy])
++ranker[fx];
return true;
}
bool isConnected(int x, int y) {
int fx = find(x), fy = find(y);
return fx == fy;
}
bool disConnect(int x) {
parent[x] = x;
return true;
}
};
|
例题
5941. 找出知晓秘密的所有专家
随机化快速排序
快速排序使用分治法(Divide and conquer)策略来把一个串行(list)分为两个子串行(sub-lists)。通过随机化的快排,选取 nums[begin] 与 nums[end] 中的随机一个元素作为主元,然后再进行划分,就可以得到一个平衡的划分,它的平均运行时间是$O(nlogn)$。
模板
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
class QuickSort {
private:
void sort(vector<int>& nums, int begin, int end) {
if (begin >= end)
return;
// 随机选取一个元素与首元素进行交换,作为pivot
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
int a = begin + rand() % (end - begin);
swap(nums, a, begin);
int i = begin, j = end;
int pivot = nums[i];
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && nums[j] >= pivot)
--j;
if (i < j) {
nums[i] = nums[j];
++i;
}
while (i < j && nums[i] <= pivot)
++i;
if (i < j) {
nums[j] = nums[i];
--j;
}
}
nums[i] = pivot;
quickSort(nums, i + 1, end);
quickSort(nums, begin, i - 1);
return 0;
}
void swap(vector<int>& nums, int a, int b) {
int temp = nums[a];
nums[a] = nums[b];
nums[b] = temp;
}
};
|
例题
215. 数组中的第K个最大元素






 WayneZ:~$ cd /home/
WayneZ:~$ cd /home/